
|
|
What is mitigation
There are several proven methods to reduce radon in your home, but the one primarily used is a vent pipe system and fan, which pulls radon from beneath the house and vents it to the outside. This system, known as a soil suction radon reduction system, does not require major changes to your home. Sealing foundation cracks and other openings makes this kind of system more effective and cost-efficient. Similar systems can also be installed in houses with crawl spaces. Radon contractors can use other methods that may also work in your home. The right system depends on the design of your home and other factors.
Types of radon reduction systems (RRS)
|
| Sub-Slab
|
| Sub-Membrane
|
|
Sub-slab RRS is deployed in the house with slab-on-grade foundation type. You can tell that you have this foundation type if, for example, you have a full basement (finished/not finished).
Sub-slab RRS usually consist of a PVC pipe installed through the slab and through the wall to the outsdide connecting to the fan and exhaust pipe.
|
Sub-membrane RRS is designed to accomodate houses with crawl space underneath the floor.
This type of system usually is very similar to the Sub-Slab type with one exception: instead of penetration through the slab the vent pipe is installed under a special membrane. Membrane is installed in the crawl space sealing off the conditioned space from soil generated gases.
|
Installation of Sub-Slab RRS
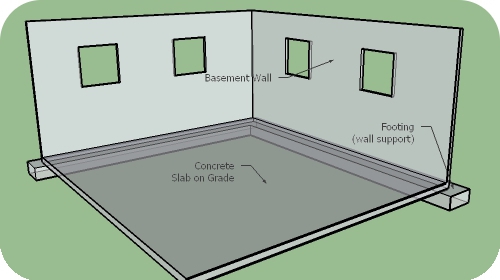 Fig. 1. Typical basement
Fig. 1. Typical basement
|
Most sub-slab systems are installed in the basement (Fig. 1).
The soil gases including Radon penetrate into the house through the cracks in the slab. It is possible to treat soil gas penetration by gaining access to the gravel/dirt under the slab and venting the gases out.
|
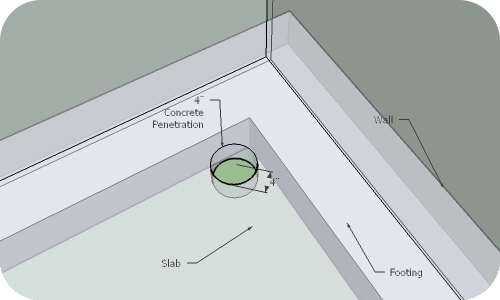 Fig. 2. Suction point
Fig. 2. Suction point
|
After assesing the structure's interior/exterior we determine the position for the 4" round slab penetration.
It is important to chose a place as close to the footing as possible. Becasuse it provides for greater reach of negative pressure all around the perimeter of the slab.
After the hole is in place we remove agregate from under the slab in vicinity of the hole, which creates a place for soil gases to "pool" around the suction point.
|
 Fig. 3. Pipe is installed through the wall
Fig. 3. Pipe is installed through the wall
|
Finally 4" PVC Pipe (SCH 40) is installed through the openings in the slab and the wall to the outside.
All joints and cracks are sealed to provide suction. After the pipe is routed to the exterior the fan and exhaust pipe are installed.
|
Installation of Sub-Membrane RRS
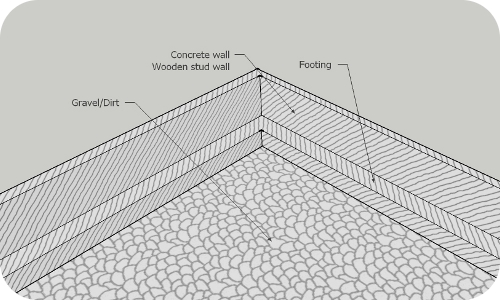 Fig. 4. Typical crawl space
Fig. 4. Typical crawl space
|
Sub-membrane type radon reduction systems are installed in crawl spaces.
Crawl space is typically about 3'-4' tall and located under the house. The base for crawl space is typically dirt or gravel. Perimeter of crawl space is lined with concrete footings on which wooden stud wall or concrete wall is resting.
Radon, as well as other soil gases, enters living area through the floor itself.
|
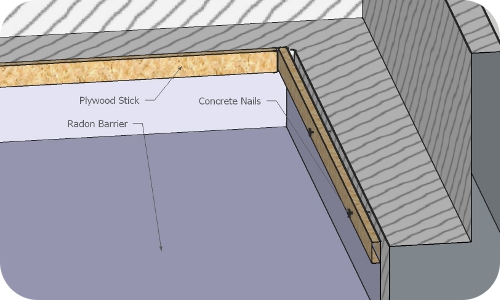 Fig. 5. Membrane is installed
Fig. 5. Membrane is installed
|
In order to collect soil gases we install membrane.
We use specifically designed Radon Barrier for our membrane. Membrane is then sealed with special caulking and mechanically fastened to the footing or the wall with strips of plywood and concrete nails.
Every single seam and joint has an air-tight seal. Any obstacle is air-tight sealed around.
|
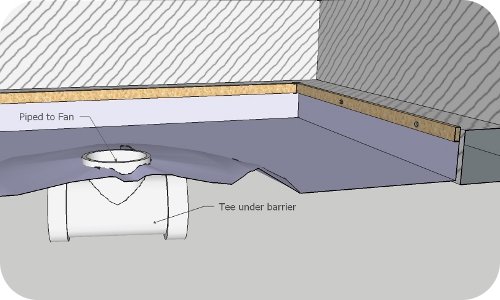 Fig. 6. Suction point is installed
Fig. 6. Suction point is installed
|
After installing the membrane we lay out piping throughout crawl space with suction points installed as 4" Tee's.
Suction points are piped together and routed outside either through the wall to outside, or (if possible) through inside wall into the attic, where fan is installed.
|
Other types
Other types of systems are possible. For example a mix between sub-slab and sub-membrane types of systems is necessary when foundation type of the house is mixed.
Please look at some pictures here.
|